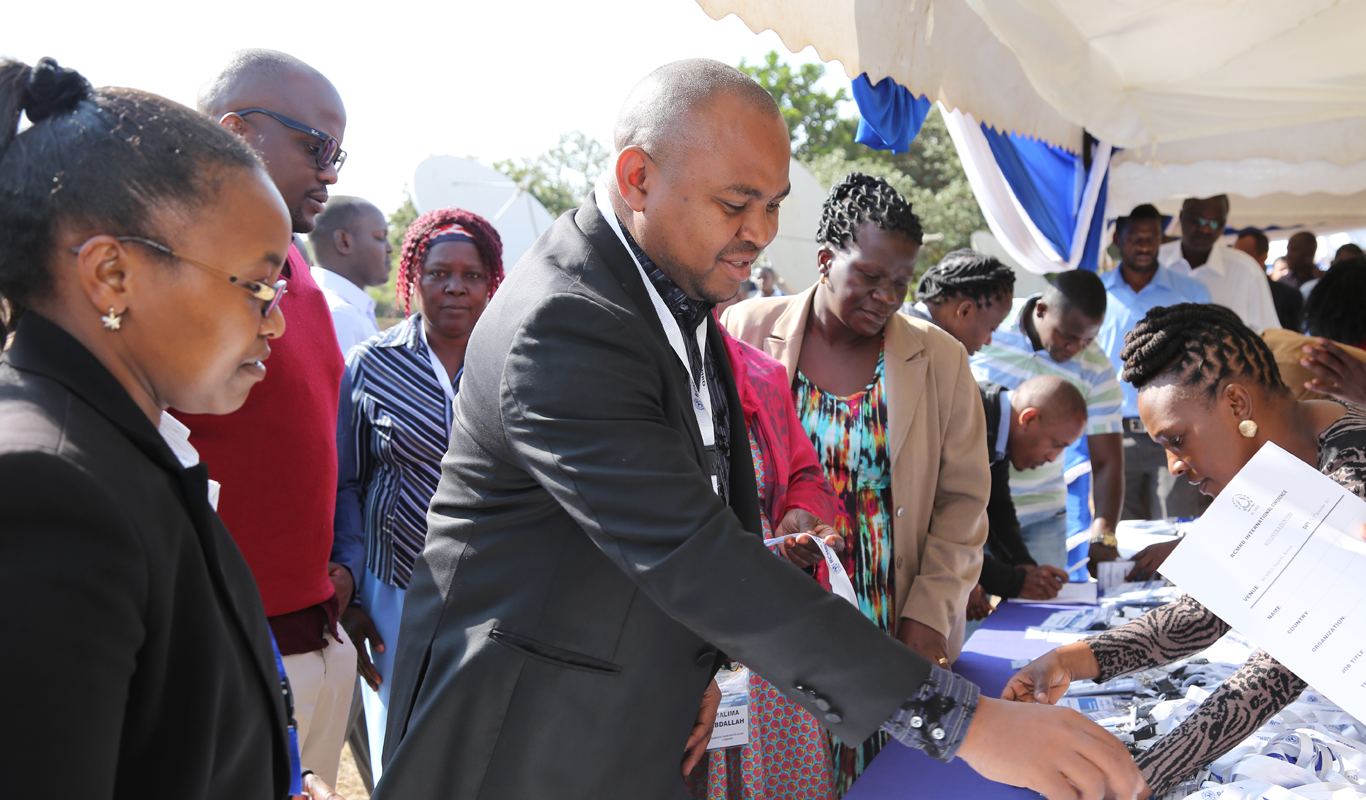
RCMRD will hold its annual RCMRD INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE on 8th to 10th August 2023 at RCMRD, Nairobi Kenya.
Read More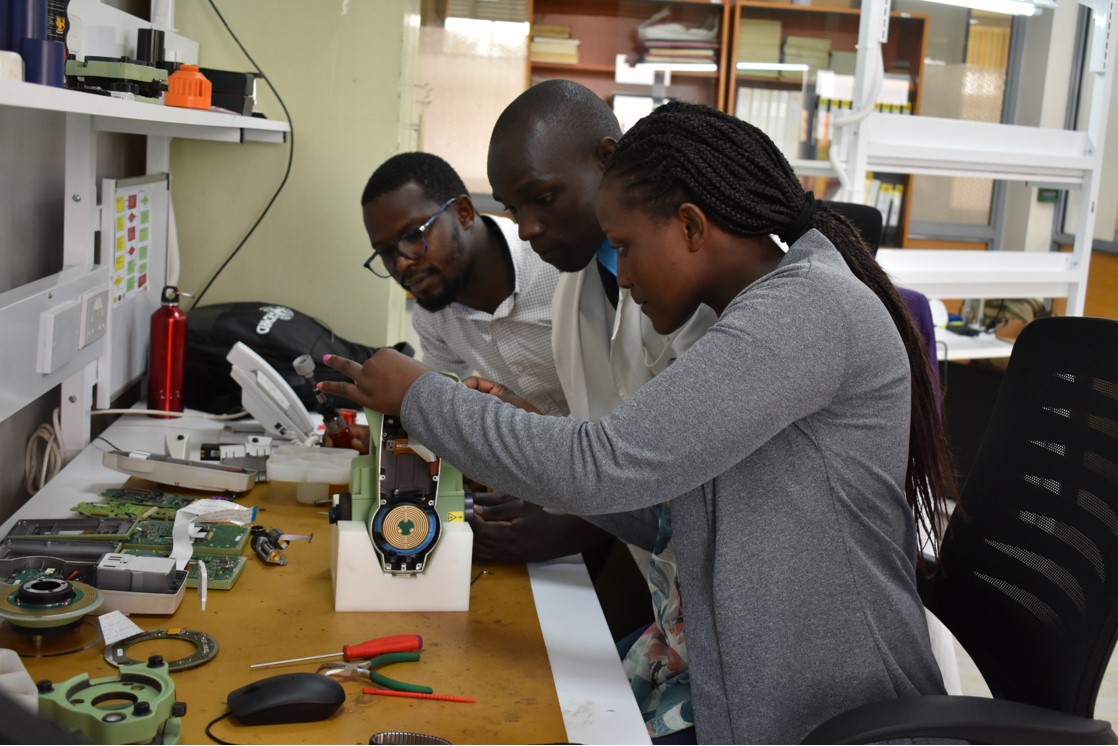
Our Engineering Department offers a wide range of technical service on Geosystems Equipment. We provide quality services such as calibration services, repair services, certification services, upgrading services and training services.
Read More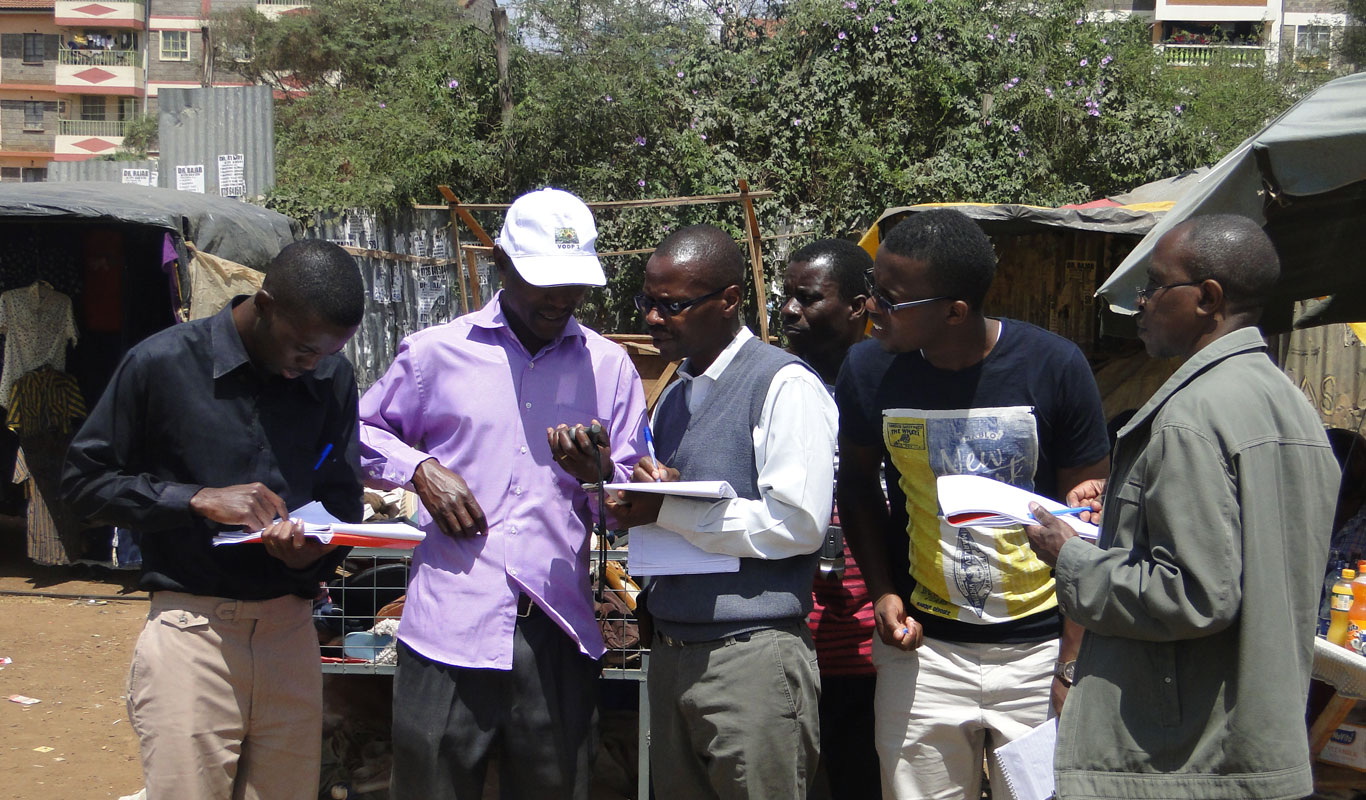
We offer expertise in PROJECT IMPLEMENTATION and ADVISORY SERVICES that are oriented towards sustainable applications in natural resource management, infrastructure and environmental management utilizing Geo-Information Technologies.

We wish to announce RCMRD Map Competition 2023 Edition that will run from 28-June-2023 to 17-Nov-2023. The theme of the competition is "Environmental and Biodiversity Conservation Efforts to Protect our Natural Resources". The total prize tag is Euros: 12,000
Read More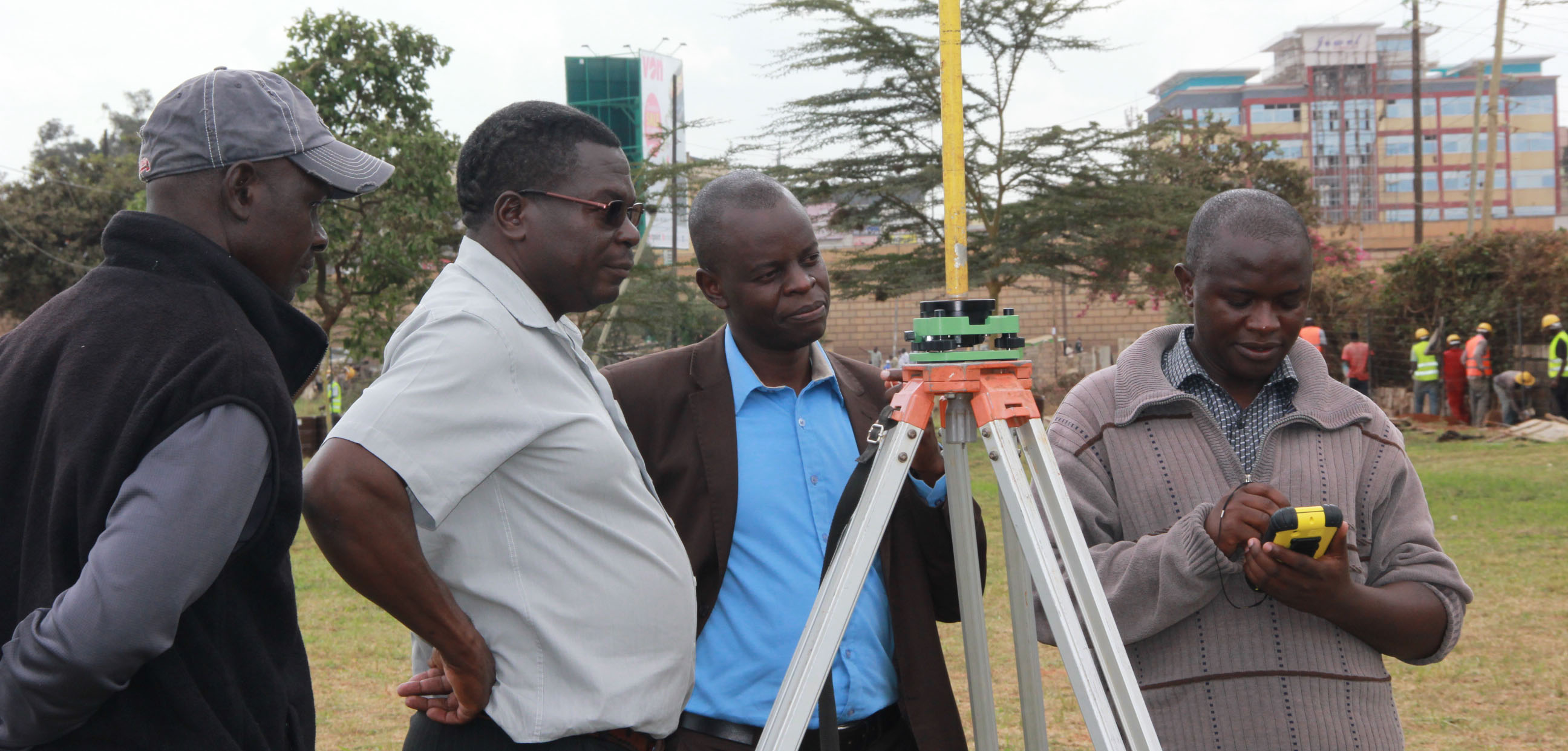
We offer SURVEYING AND MAPPING expertise in Topographical surveying, Engineering surveying, Hydrographic surveying, Cadastral surveying, Control surveying and Training in Land survey related short courses such as GNSS Training, Total station training, leveling among others.
Read More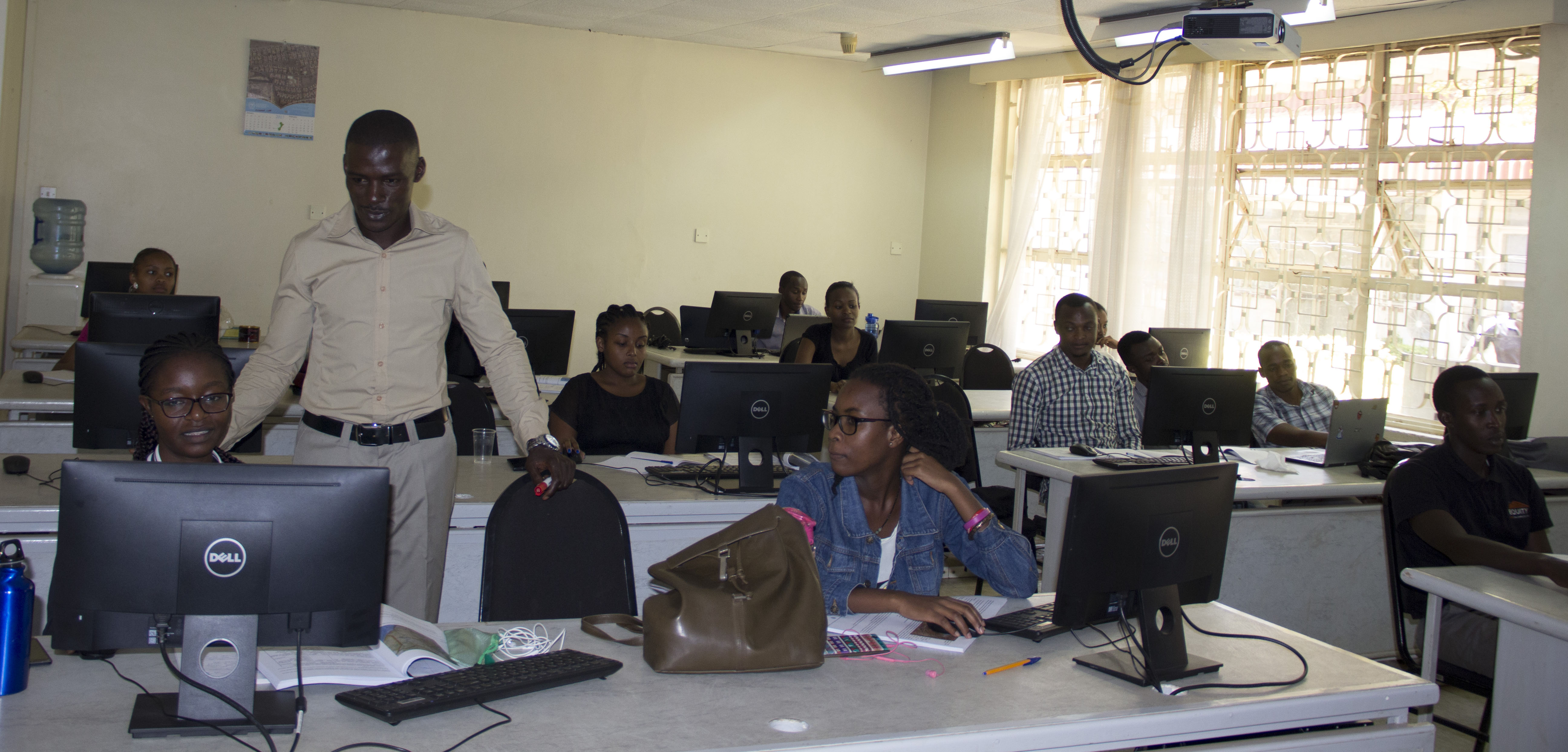
We offer PROFESSIONAL SHORT COURSES in areas such as Remote Sensing & Satellite Image Processing/Interpretation, Geographic Information Systems (GIS), Global Positioning/ Navigation Systems (GPS), Information Technology, Surveying etc.
Read More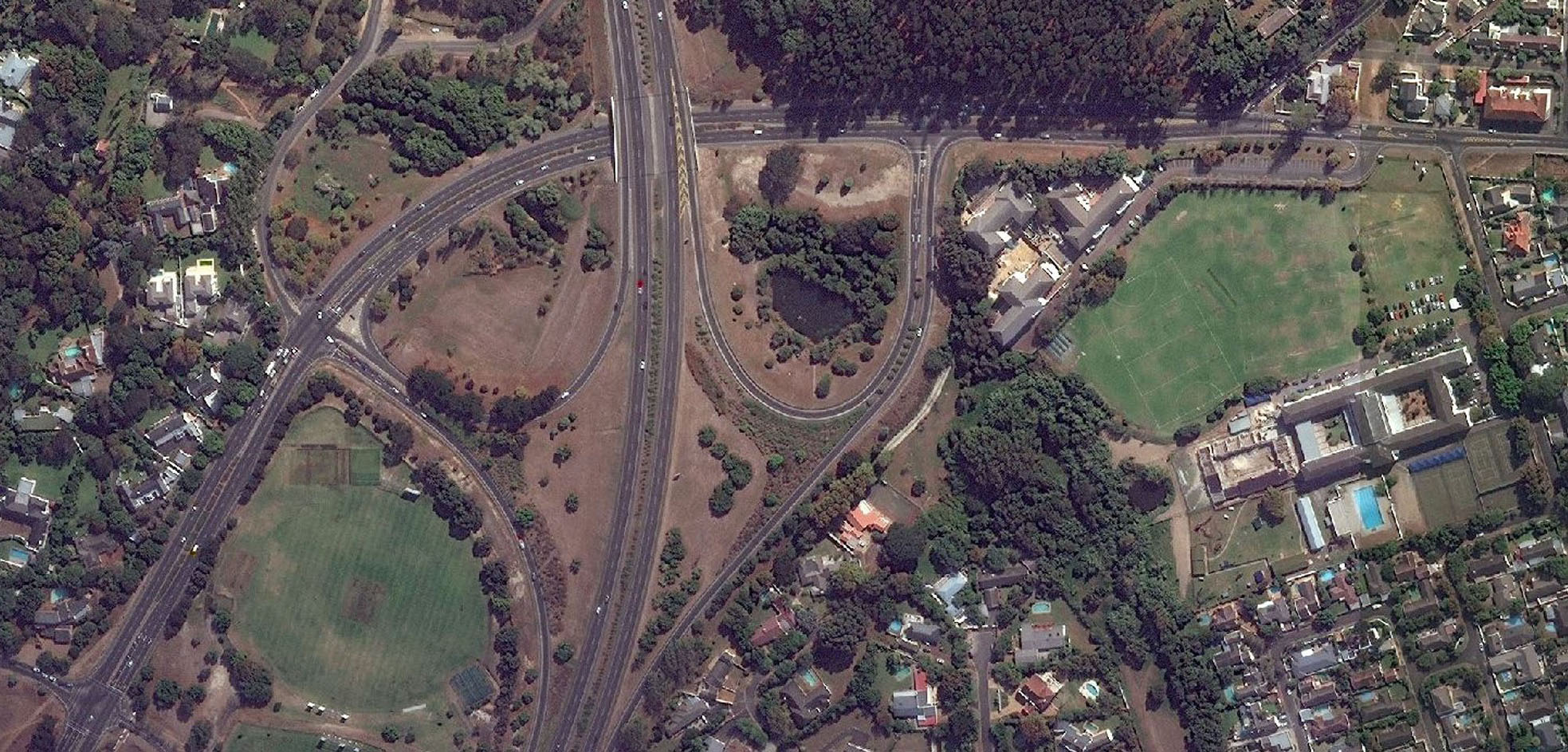
We offer SATELLITE IMAGERY DATA PRODUCTS i.e. High Resolution Satellite Imagery data with ground sampling rate below 5 meters, Medium Resolution Satellite Imagery data with ground sampling rate between 5 – 250 meters and Low Resolution Satellite Imagery data with ground sampling rate above 250 meters
Read More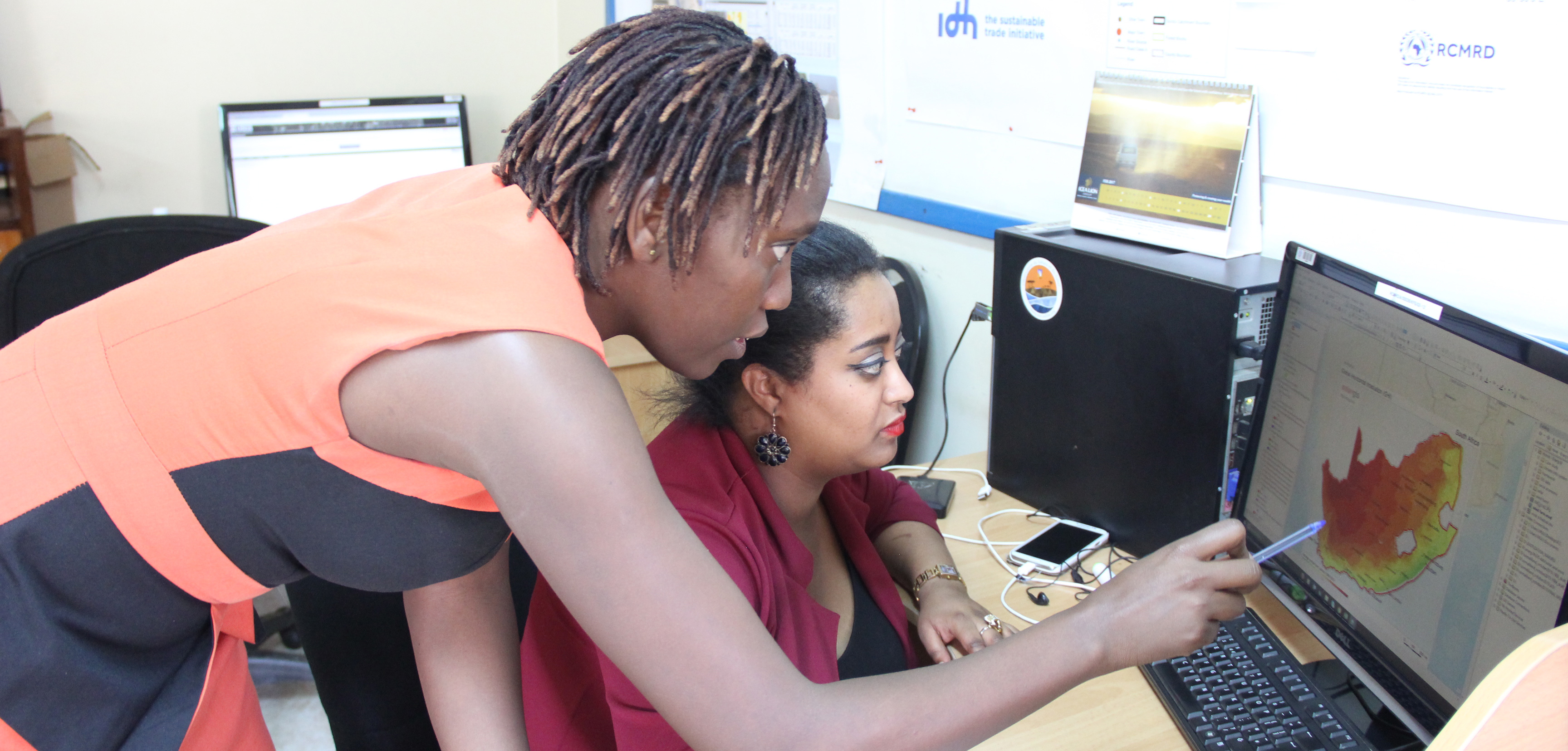
For users to access the DATASETS AND MAPS that have been developed and shared online, we have platforms such as apps portal, geoportal, open data site that are useful for accessing these spatial based products and services
Read More


Intake
Through Out the Year
Intake
Through Out the Year
Intake
Through Out the Year
Roysambu, Kasarani
Nairobi, Kenya
+254 020 2680748 / 2680722
+254 723 786161 / +254 735 981098
P.O. Box 632-00618 Nairobi, Kenya
rcmrd@rcmrd.org